Elevate Your BI with Data Warehouse Architecture
In today’s data-driven world, It should not come as a surprise that each of us will produce 1.7 MB of data per second sooner rather than later. And having a Data warehouse becomes super important.
Making more intelligent business decisions is a distinctive aspect that determines your organization’s long-term performance in today’s hyper-competitive, data-driven business climate. Data warehouses are essential to an organization’s ability to remain competitive and use data to inform decisions on creating new goods, market to customers, and promote cross-functional business.
A modern data warehouse’s structure and constituent parts are known as data warehouse architecture. As technology advances and the needs of the data-driven economy increase, the multi-cloud architecture enables mobility to move workloads and data as the business grows.
In this blog article, we’ll define, link, and compare data warehousing and consulting. We’ll also show you how we have excelled in data warehouse services and data warehouse consulting. But let’s start with some basic explanations.
What is BI Architecture?
When using computer-based techniques and technology to construct business intelligence systems for online data visualization, reporting, and analysis, the phrase “Business Intelligence Architecture” is used to specify standards and regulations for data organization.
Data Warehousing is a component of the BI architecture. A Data Warehouse, which is regarded as the core element of business intelligence, is used to organize, store, clean, and extract the data from its central repository, which is considered the fundamental component of business intelligence.
What is Data Warehouse Architecture?
An approach to defining the total architecture of data exchange, processing, and presentation that exists for end-client computing within the organization is the Data Warehouse Architecture. Although every data warehouse is unique, they all share certain essential standards.
A central concept in Data Warehouses is the ETL process:
Extract: Collecting information from a variety of disparate sources.
Transform: Making imperfect data into usable, clean, structured, and verifiable data.
Load: Loading the information onto a new location.
the data and what sources they will require.
Components of Data Warehouse Architecture
The following are the several layers of DWH architecture’s components:
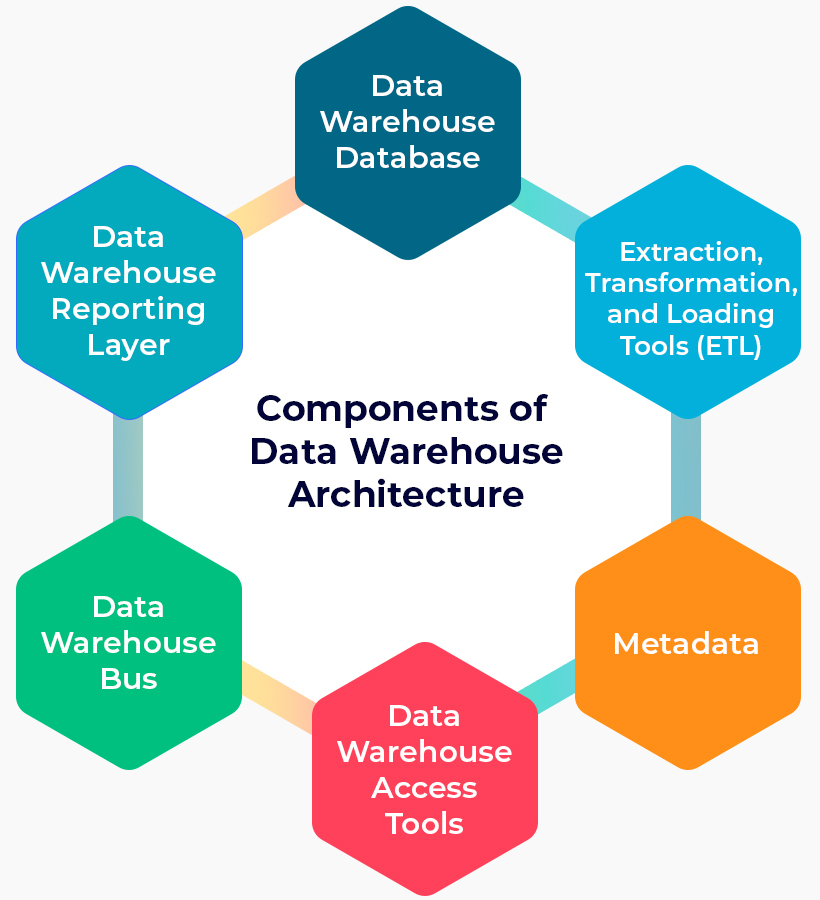
I. Data Warehouse Database
A database that stores all organizational data and makes it accessible for reporting is the crucial feature of a DW architecture. This implies that you must decide on the type of database you’ll use to keep information in your warehouse.
There are following four types of Databases:
- Typical Relational Databases: The row-centered databases you regularly use, such as SAP, Microsoft SQL Server, IBM, Oracle, and DB2.
- Analytics databases: Greenplum and Teradata are two examples of analytics databases specifically designed for data storage to support and manage analytics.
- Data warehouse applications: Although data warehouse applications aren’t strictly storage databases, many dealers now provide programs that include both hardware for storing data and software for data management. A few examples include SAP Hana, IBM Netezza, and Oracle Exadata.
- Cloud-based databases: You aren’t required to buy any hardware to set up your data warehouse because cloud-based databases, like Microsoft Azure SQL, Amazon Redshift, and Google Big Query, can be stored and accessed on the cloud.
II. Extraction, Transformation, and Loading Tools (ETL)
Central to the structure of a corporate data warehouse are ETL tools. These tools help collect data from many different places, organize it correctly, and load it into a data warehouse.
Your choice of ETL tool will determine:
- The duration of data extraction
- Methods for data extraction
- The kind of modifications used and how easily they were carried out
- Definition of business rules for data cleansing and validation to enhance end-product analytics
- Completing lost data
- Describe the flow of information from the primary depository to your business intelligence apps.
III. Metadata
Metadata provides a foundation for data and explains the data warehouse database in a DW architecture. It aids in creating, maintaining, processing, and utilizing the data warehouse.
Data warehousing uses two types of metadata:
Technical Metadata consists of data that managers and developers can use to carry out warehouse development and management duties.
Business Metadata consists of details that provide an understandable perspective on the data kept in the warehouse.
IV. Data Warehouse Access Tools
A database or database collection serves as a data warehouse’s basis. Companies that employ data warehouses can’t deal with databases without the aid of tools unless they also have access to database administrators. However, not all company units are like that. For this reason, they work with several no-code data warehousing systems, including:
- Users can create corporate reports for analysis using Query and Reporting Tools, which might take the form of spreadsheets, formulas, or interactive visualizations.
- With the aid of Application Development Tools, customized reports may be produced and presented in interpretations for reporting needs.
- Utilizing cutting-edge statistical modeling techniques, Data Mining Tools for Data Warehousing systematizes the process of finding arrays and linkages in massive amounts of data.
- OLAP Tools make it possible to build a multi-dimensional data warehouse & analyze corporate data from various angles.
V. Data Warehouse Bus
It includes a data mart and specifies the data flow within a data warehousing bus architecture. A data mart is a data access level that permits users to exchange data. Data produced for a specific user group is likewise divided using this method.
VI. Data Warehouse Reporting Layer
End users can access the BI database architecture or BI interface through the reporting layer in the data warehouse. The reporting layer of the data warehouse acts as a dashboard for visualizing data, making reports, and pulling out any needed data.
IV. This is why you need Data Warehouse Architecture Service in your Organization.
Running a data-driven organization in a rapidly evolving changing business landscape, data warehouses are appropriate and the best and most effective way to win.
The most accurate and dependable method for companies to store and access structured data is through data warehouses, which enhances cross-organizational data access through reports, dashboards, and analytics tools. These enable organizations to make better decisions and better performance monitoring because they are confident in the reliability of their data. This starts a positive cycle:
Consider this hypothetical situation (sadly common in the real world): Company A owns a lot of data, but it isn’t easy to access. Report generation takes a while, and users can’t always rely on the outcomes; perhaps quarter-end reports don’t line up, or some of the company’s more giant data puzzle is missing. Such reporting deficiencies only aggravate friction in the organization’s data, social, collaborative, and workflow systems, to name a few.
Now consider the opposite situation: Company B has set up a data warehouse so they can access data accurately, conveniently, and whenever needed. Users will read predefined reports at businesses like this, and as their interest is stimulated, they will ultimately ask for more. They will begin to conduct experiments to enhance operations, improve the overall customer insight, or save money, to name a few potential outcomes, once they realize how easy it is to receive pertinent departmental and/or company data. This would promote risk-taking and ultimately transform the company.
In every area—from product development, marketing, pricing, production processes, historical analysis, forecasting, employee organization, and customer satisfaction—organizations with dedicated data warehousing teams can plan and advance far ahead of their less data-savvy competitors. In other words, they can succeed where others will struggle.
When looking for insights, it’s critical to decide which type of database your organization requires and how you intend to use it. When considering your data warehouse architecture, it is also crucial to consider who will review it.
V. What are various Data Warehouse Services Offered by Beyond Key?
Data Warehouse Services
In this Beyond Key team takes on:
- Development and configuration of a data warehouse.
- Integration of the data warehouse with the current infrastructure (data sources, BI, and data analytics infrastructure).
- Data cleansing and migration.
- Ongoing administration and support of the data warehouse.
- Configuring a data warehouse on demand.
Data Warehouse Consulting
- Engineering DWH requirements.
- We offer the following data warehouse consulting services with the help of our Experts Data Warehouse Consultants. Solution design for DWH
- Making a business case.
- The architecture of the DWH solution.
- The best cloud data warehouse platform, an outline of it, and its configuration.
- Designing data governance for data security, availability, and quality.
- Designing ETL/ELT, data modeling, etc.
- Plan for DWH migration, implementation, and optimization.
- Support from consultants or complete project management.
Data Warehouse Migration
We assist you in migrating your current on-premises data warehouse to the cloud without affecting business operations, which helps you improve DWH performance and reduce the total cost of ownership.
We assist you in creating a hybrid data warehouse or moving your existing DWH solution to the cloud by:
- Sketching out a migration strategy and plan.
- Creating a cloud data warehouse design.
- Helping you choose the best cloud provider.
- Optimizing costs by configuring the cloud cluster.
- Updating an existing data warehouse on a new system.
- Combining the cloud and on-site environments.
- Adding metadata and master data to the new data warehouse.
- Testing the data’s completeness to make sure the migration is successful.
Data Warehouse Testing
A complete DWH testing package, which may also include security testing, ETL/ELT testing, BI testing, and performance testing.
Beyond Key’s testing services have the following stages:
- Studying the demands of the project.
- Planning and designing tests.
- Implementation of tests.
- Analysis of the results and responsibility.
Data Warehouse Support
We offer DWH support to assist you in locating and resolving DWH performance issues, achieving DWH stability for reliable and timely data delivery to business users, and reducing DWH processing and storage costs.
Steps covered by support include:
- Architecture optimization for DWH solutions.
- The improvement of specific DWH tools (keeping more data in memory, adding indexes to tune query performance)
- DWH design improvement (changing database schemas, data loading, etc.).
Conclusion
Data Warehousing is not a new phenomenon. All big organizations already have it, but they are just not incorporated correctly. The reason is improper Data Warehousing architecture. With a high-quality data warehousing architecture, you understand and outline strategies for successful and efficient data warehousing.
The catch is the architecture’s heavy influence by variables like the data’s worth, the technologies’ efficiency, and the deployed hardware’s physical constraints. Knowing these dependencies, along with their properties and characteristics while constructing the data warehouse’s architecture, is crucial. Because once you do that, it yields a Data warehouse that ensures data consistency and helps you make excellent business decisions.