A Complete Guide to Data Warehouse Implementation
This guide shows you the complete process of data warehouse implementation. We start with the basics: what is a data warehouse? Then, we look at its key components, or parts. We also list the essential steps to make your project work. You will learn about new trends, common problems, and the best ways to get it right. This helps your company use its data. The goal is to make smarter, faster decisions.
Introduction to Data Warehouse Implementation
Businesses today are swimming in data. It comes from all over the place. To stay ahead, you must understand that data. This is why we use a data warehouse. But just buying a data warehouse product does nothing. You need a plan.
A proper data warehouse implementation is the key. This process turns messy, raw data into a real tool for growth. So, understanding what is data warehouse implementation is your first step. It’s how you build a system that gives you clear answers. This process makes one single, trusted place for your data (a ‘source of truth’).
This one source helps with daily reports and big-picture strategy. It’s a very important investment for any data warehouse for your businesses that wants to use data well.
What is Data Warehousing?
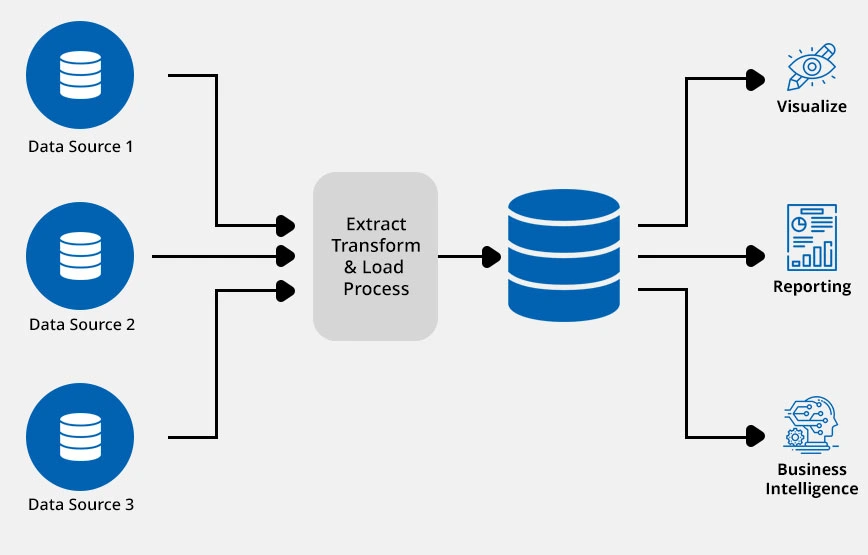 A data warehouse is a special kind of system. It is built to store and manage huge amounts of data from many different sources. It’s not like your regular database, which just handles daily transactions (like sales). A data warehouse is different; it’s built specifically for analysis and reporting.
A data warehouse is a special kind of system. It is built to store and manage huge amounts of data from many different sources. It’s not like your regular database, which just handles daily transactions (like sales). A data warehouse is different; it’s built specifically for analysis and reporting.
Think of it like this: a normal database is like a busy kitchen’s order ticket system, focused on what’s happening right now. A data warehouse is like the restaurant’s main pantry. It stores all the ingredients (data) collected over time, neatly organized in one place, ready for you to analyze and create reports.
It collects and organizes data into one, single view. This makes it much easier for companies to find trends and get insights. The main goal of any data warehouse implementation is to support business intelligence (BI) work.
This helps leaders make good decisions based on data that is clean, correct, and shows history. This is a basic part of learning how to implement data warehouse solutions the right way.
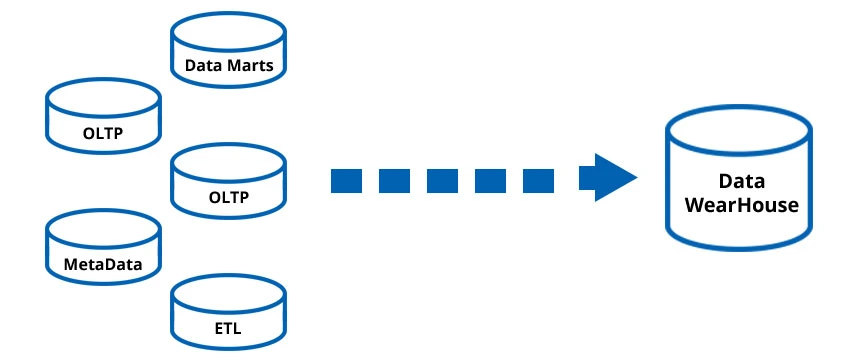
Key Components of a Data Warehouse
To do this project right, you need to know the building blocks. Each component, or part, has a special job. Each one helps change raw data into useful insights. When you ask what is data warehouse implementation, you are really asking how these parts work together. They must work together to make one strong, efficient system. Here are the main components:
- Data Sources: This is where your data begins. It includes sales systems, CRM software (for customer info), simple spreadsheets, and even data you get from outside your company.
- Data Staging and ETL Tools: The staging area is a temporary holding spot. Data goes here to be prepared. ETL (Extraction, Transformation, Loading) tools do the hard work. They pull data from the sources, clean it, and load it into the warehouse.
- Data Warehouse Database: This is the main storage, the big pantry. This is where the clean, processed data lives. It can be a classic database, a new cloud database, or a special database built for very fast analysis.
- Metadata: This is “data about your data.” It’s like a label on a jar. Metadata explains where the data came from, what it means, and how it connects to other data. This is very important for both tech teams and business users.
- Data Marts: These are like small, focused mini-warehouses. They are built for just one department, like sales or marketing. Data marts make it easier for teams to find the exact data they need, fast.
- Access and Reporting Tools: These are the tools your people will actually use. This includes BI platforms, reporting software, and other apps that let users ask questions, analyze the data, and make charts and dashboards.
How to implement data warehouse – Key Steps in Data Warehouse Implementation
 A good project needs a clear path. You can’t just start building. A strong data warehouse implementation plan is what makes sure the final system actually meets your business goals and gives you real value.
A good project needs a clear path. You can’t just start building. A strong data warehouse implementation plan is what makes sure the final system actually meets your business goals and gives you real value.
So, what is this process? The job of what is data warehouse implementation can be broken into a few clear steps. You start with planning and you finish with support. Following these data warehouse implementation steps is how you avoid common mistakes and keep the project moving forward.
1. Requirement Gathering and Feasibility Study
First, you must understand why you are doing this. What does the business need? This means you talk to stakeholders (the people who will use it). You must define the goals, find all the data sources, and check if the project can even be done (the feasibility study). If you don’t get the requirements right, the whole data warehouse implementation will fail. This is the foundation.
2. Designing the Data Warehouse Architecture
Now you draw the blueprint for your system. This includes making a data model. A data model (like a star schema or snowflake schema) is just a plan for how to organize the data. In this step, you also plan the ETL processes. And you pick the right technologies. What will you use for storage? What tools will people use to access the data? A good data warehouse architecture is vital. It must be able to grow (scalability) and run fast (performance).
3. Data Integration and ETL Development
This is the hardest part. This is where the real work happens. Data is extracted (taken) from its sources. Then it is transformed (changed) into a format that is the same for everything. Finally, it is loaded into the warehouse. This step also includes cleaning the data to make sure it is high quality. You also apply business rules to get it ready for analysis. A good data warehouse implementation plan always puts a lot of time and money into this ETL phase.
4. Building Data Marts
The main warehouse is huge. To make data easier to use, you can build data marts. Remember, these are the smaller, focused “mini-warehouses” for specific departments. This lets the sales team, for example, look at only sales data. They don’t have to search the entire warehouse. This is a key part of a smart what is data warehouse implementation.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
You cannot skip this. Before anyone uses it, you must test everything. Does this query run fast enough? Is the data correct? Is the system secure? You must also let the real users test it. This is called User Acceptance Testing (UAT). The UAT checks if the system actually does what the users asked for. Trust me, this is a critical checkpoint in any data warehouse implementation plan.
6. Deployment and Maintenance
After all tests pass, you deploy the data warehouse. It goes live for the business to use. But the project is not over. Not at all. The work never really stops. You will always need ongoing maintenance. You have to watch performance, fix bugs, and update the system when the business changes. A successful data warehouse implementation must include a plan for this long-term support.
Data Warehouse Implementation Trends
This field changes fast. Data warehousing is always evolving. You need to know the new trends. This helps you build a solution that works today and works tomorrow. These trends are changing the answer to what is data warehouse implementation. They change how companies plan their data strategy.
- Cloud-Based Data Warehousing: This isn’t really a “trend” anymore. It’s the new standard. Platforms like Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift offer amazing growth (scalability) and flexibility. A recent Gartner report showed over 75% of new data warehouse projects are cloud-native. You just pay for what you use. A Modern Data Warehouse is almost always in the cloud.
- Real-Time Analytics: Business moves fast. People need insights now, not next week. Modern data warehouses are now built to handle real-time data. This lets companies make decisions based on what is happening this very second. Think of a logistics company tracking packages in real time to re-route drivers. That’s the goal.
- Integration with Big Data and AI: Warehouses used to be for neat, organized data (structured data). Not anymore. Now, they must work with all data. This means integrating with systems that handle messy, unstructured data, like in a Data Lake vs Data Warehouse setup. This connection is what lets you do advanced AI and machine learning. You can find much deeper insights this way.
- Automation and DataOps: Automation is making data warehouse implementation much easier. We’re also seeing the rise of DataOps. This is just like DevOps, but for data teams. It uses automation and better processes to help teams build and maintain data pipelines. The result is more speed and fewer errors.
Challenges in Data Warehouse Implementation
The benefits are big, but let’s be honest. A data warehouse implementation is hard. It is not an easy project. Understanding what is data warehouse implementation also means you must be ready for the problems. You will have technical problems. You will also have people problems (organizational resistance). Knowing these challenges ahead of time is the first step to making a data warehouse implementation plan that actually works.
- Data Quality: This is the big one. Garbage in, garbage out. If you put bad data into your warehouse, you will get bad reports. Ensuring data is clean, accurate, and consistent is a huge, constant challenge. In fact, many reports say data teams spend 60-80% of their time just cleaning data, not analyzing it.
- Integration Complexity: Pulling data from 20 different systems is very complex. It’s a technical nightmare sometimes. You have different data formats, different structures, and different ways to access each source. This makes the ETL development process very slow and difficult.
- Scalability: Your data will grow. Will your warehouse grow with it? It has to. The system must scale (get bigger) without slowing down. Designing for this from day one is critical, but it’s hard to predict the future.
- Cost and Resources: These projects can be expensive. The initial cost of data warehouse implementation (software, cloud bills) is high. And the ongoing maintenance costs add up. Plus, you need a skilled team of data engineers, architects, and analysts. These people are hard to find and expensive to keep.
- User Adoption: What if you build it, and nobody comes? A data warehouse is only valuable if people actually use it. If the tools are too hard to use, or if people are not trained, they will go back to their old spreadsheets. Low user adoption will kill your project’s ROI.
Best Practices for Data Warehouse Implementation
So, how do you handle those challenges? How do you make sure your project works? The best way is to follow proven best practices. These are not just theories; these are guidelines from years of real-world projects. They can be the difference between a project that fails and one that changes your whole company. Following these Best Practices for Data Warehousing is a main part of a good data warehouse implementation strategy.
- Define Clear Business Goals: Start with “why.” Always. A good data warehouse implementation is led by clear business goals, not by a cool piece of technology. What decisions do you need to make?
- Focus on Data Governance: You need rules. Start with strong data governance policies from day one. This means deciding who owns the data, who can see it, and how to keep it safe and high-quality.
- Design for Scalability: Build an architecture that can grow. It must grow with your data and be able to change when your business needs change in the future.
- Implement in Phases: Don’t try to build the entire thing at once. (We call this “boiling the ocean.”) Start small. Use an iterative approach. Build one data mart for one department first. This lets you show value quickly. You also learn lessons you can use for the next phase. This is a much smarter way to handle what is data warehouse implementation.
- Provide Training and Support: This is so important. Make sure your end-users are trained well. Show them how to use the new tools and find answers. And give them ongoing support so they don’t get stuck. This is how you get good user adoption.
Why Partnering with an Expert Matters
We have been doing this since 2008. We help companies build strong data warehouses. We know how to connect all your different data sources into one, central place. Our experienced data warehouse consultants know that a successful data warehouse implementation is not just about the software. It’s about making your data better. It’s about giving you real-time access. It’s about helping you make decisions based on numbers. We are experts at turning messy, separate data into a valuable tool for your company.
How We Help Your Data Warehouse Implementation
We offer services for the entire project. We guide you through every single stage of what is data warehouse implementation. Our main goal is to build a solution that fits your company’s exact needs. We want to deliver real, measurable results.
- Design and Research: We look at your current systems. Then we create a custom strategy for you. This plan covers technology choices, data modeling, and how to plan for growth.
- Implementation: Our experts help with all the technical work. We can automate data pipelines, manage data quality, and handle all the testing and deployment.
- Cloud Migration: We can help you move. We migrate your old, traditional systems to a modern, cloud-based data warehouse. We make sure this happens smoothly, with little to no downtime.
- Modernization: Is your current warehouse old? We can check your setup. We will recommend upgrades to make sure your data warehouse can handle modern needs, like AI.
- Support: Our team gives you ongoing support. We make sure your data warehouse keeps running smoothly. We prevent downtime and keep your analytics projects on track.
Conclusion
A data warehouse implementation, when done right, can truly change your company. It turns data from something that just sits there into a real, strategic asset. It helps you make smart decisions.
It’s a big project. But now you understand the components. You know the key data warehouse implementation steps. And you know the best practices to follow. With this, you can build a powerful system. A system that gives you one single source of truth.
Yes, there are challenges. We know that. But the rewards are much bigger. You get better data quality. You get faster, more accurate insights. The effort is worth it. Understanding what is data warehouse implementation is the first big step. It’s the start of your journey to becoming a truly data-driven company.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a data warehouse?
A data warehouse is a central place to store information. It’s built so you can analyze that information to make better decisions. It stores large amounts of data from many sources, all in one place. It is not like a normal database; it is built for querying and reporting. It is the “single source of truth” for a company’s data.
2. What is data warehouse implementation?
Data warehouse implementation is the full process of building and launching a data warehouse. It starts with planning and designing. It includes getting all the data, cleaning it, and loading it. It ends with deploying the system and setting up the tools for analysis. A good implementation gives the business trusted, high-quality data.
3. What are the steps of data warehouse implementation?
The main steps are:
1) Gathering requirements (finding out what the business needs).
2) Designing the architecture and the data model.
3) Building the ETL processes to move and clean the data.
4) Cleansing and checking the data.
5) Building data marts (if needed).
6) Testing everything.
7) Deploying the system and then doing maintenance.
4. What are the four stages of data warehouse?
The four main stages are:
1) Data Sourcing (getting data from all your systems).
2. Data Staging (where the ETL process happens: extracting, transforming, and cleaning).
3) Data Storage (where the clean data lives in the main warehouse).
4) Data Access (where your users use BI tools to get reports and insights).
5. What are the key components of a data warehouse?
The key components are: the data sources, the staging area (for ETL), the main database (storage), metadata (data about data), data marts (for specific teams), and the access tools (like BI platforms) that people use to see the data.
6. How to implement data warehouse?
To implement a data warehouse, you must start with clear business goals. Then, design an architecture that can grow. Pick your tools. Build and test your ETL pipelines to move and clean the data. Launch the solution one step at a time (in phases). Finally, train your users and have a plan for long-term support and data governance.
7. Cost of data warehouse implementation?
The cost of data warehouse implementation changes a lot. It can be from $50,000 to over $2,000,000. The final price depends on many things: how much data you have, if you build it on-premises or in the cloud, software license costs, how big your team is, and how much ongoing support you will need.






 A data warehouse is a special kind of system. It is built to store and manage huge amounts of data from many different sources. It’s not like your regular database, which just handles daily transactions (like sales). A data warehouse is different; it’s built specifically for analysis and reporting.
A data warehouse is a special kind of system. It is built to store and manage huge amounts of data from many different sources. It’s not like your regular database, which just handles daily transactions (like sales). A data warehouse is different; it’s built specifically for analysis and reporting. A good project needs a clear path. You can’t just start building. A strong
A good project needs a clear path. You can’t just start building. A strong